Simcenter Amesim 2022.1_Libraries and Solutions
New Version
작성자
플로우마스터코리아
작성일
2022-09-01 17:18
조회
2353
Simcenter Amesim 2022.1 [Libraries and Solutions] 에서 사용할 수 있는 모든 새로운 기능과 업데이트를 안내합니다.
| 1. Thermal and lubrication | |||||||||
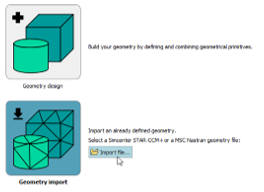
| ◎ Embedded CFD Cabin Geometry import | |||||||||
| Heat Exchanger Assembly Tool library |
|||||||||
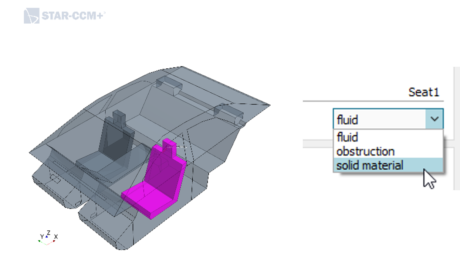
| Import of an existing geometry (.sim or .nas) into the Embedded CFD Cabin workflow Definition of each imported volume as fluid domain, solid thermal material or obstruction | |||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Save time by reusing an existing geometry | |||||||||
| ● Improve model fidelity to actual geometry | |||||||||
| ● Keep your usual Embedded CFD workflow for both imported and parametric geometry | |||||||||
 |
 |
 |
|||||||
| Geometry import is now available | Set volumes as fluid, solid or obstruction |
Your geometry is ready to use in a few clicks |
|||||||
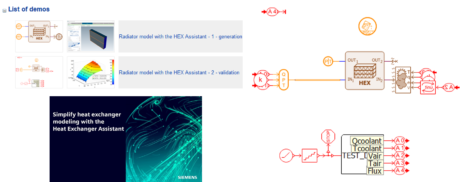
| ◎ Radiator model with the HEX Assistant demo | |||||||||
| Thermal Management solution | |||||||||
| A new demonstrator with videos shows how to create and validate a plate and fins radiator type heat exchanger based on design and test data with the HEX Assistant | |||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Learn how to create a radiator model from the data to the validated component |
|||||||||
| ● Reproduce and customize the workflow thanks to available videos showing all the steps |
|||||||||
| ● Leverage all Simcenter Amesim features to save time and ultimately focus on the design activities |
|||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| Available in heat exchanger systems solution demos | Workflow based demos with videos at each step | ||||||||
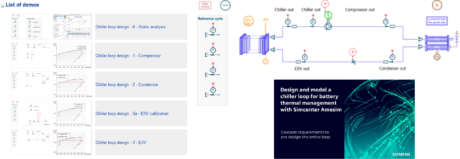
| ◎ Chiller loop design demo | |||||||||
| Thermal Management solution | |||||||||
| A new demonstrator with videos shows how to design a refrigerant loop dedicated to chilling a coolant from the predesign of the cycle to the detailed geometrical model of heat exchangers | |||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Learn how to design a refrigerant loop with Simcenter Amesim from the specification to the detailed model | |||||||||
| ● Reproduce and customize the workflow thanks to available videos showing all the steps | |||||||||
| ● Leverage all Simcenter Amesim features to save time and ultimately focus on the design activities | |||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| Available in electric vehicle integration solution demos | Workflow based demos with videos at each step | ||||||||
| ◎ Plastics in thermal library | |||||||||
| Thermal library | |||||||||
| - Users now have direct access to plastic materials without providing their own data | |||||||||
| - The materials are set with constant properties for a standard range usage | |||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Access various plastic thermal properties directly from the library database | |||||||||
| ● Easily include plastic parts in thermal management models | |||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| Available in thermal solid properties submodel (THSD00) | The following materials are now ready to use | ||||||||
| ◎ Modular piping generic segment | |||||||||
| Thermal Hydraulic and Pneumatic libraries | |||||||||
| - Definition of a generic segment through modular piping technology | |||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Include nonstandard piping geometry (or any device) in the modeling piping component | |||||||||
| ● Benefit from the simplified modeling level to reduce CPU time while keeping the same level of accuracy | |||||||||
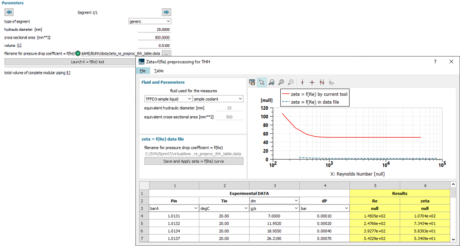
| ● Directly use your pressure drop data with a user-defined zeta=f(Re) table and a dedicated tool to generate it | |||||||||
 |
 |
 |
|||||||
| Where to find the new segment definition |
New segment type : generic pipe | Zeta=f(Re) table generation tool | |||||||
| ◎ Heat Exchanger Assistant | |||||||||
| Thermal library | |||||||||
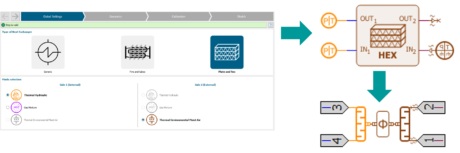
| A. You can access various types of heat exchanger : | |||||||||
| - Generic heat exchanger | |||||||||
| - Fins & tubes heat exchanger | |||||||||
| -Plates & fins heat exchanger | |||||||||
| B. The following libraries are available : | |||||||||
 |
|||||||||
| C. Define your heat exchanger in 4 steps | |||||||||
| D. Generate the corresponding model automatically | |||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| How to launch the tool | Speed up your workflow with the heat exchanger assistant |
||||||||
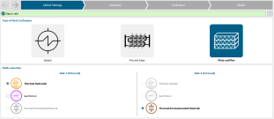
| Features | |||||||||
| ● Complete workflow to build your heat exchanger model | |||||||||
| ● Interactive tool to set the geometry and thermal correlations | |||||||||
| ● NTU regression tool to calibrate the heat exchange based on test data | |||||||||
| ● Automated sketch generation | |||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Speed up the workflow to create your heat exchanger model | |||||||||
| ● Avoid any parameter errors with clear visualizations | |||||||||
| ● Calibrate your heat exchanger with experimental data | |||||||||
| ● Quickly size your heat exchanger with a study on the geometrical parameters | |||||||||
 |
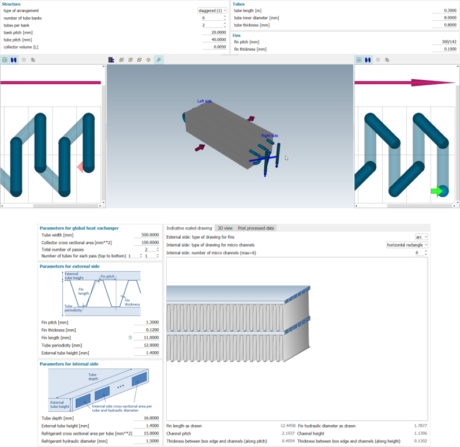 |
||||||||
| Quick heat exchanger definition | User-friendly geometry setting | ||||||||
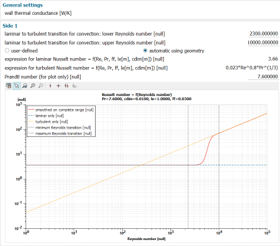 |
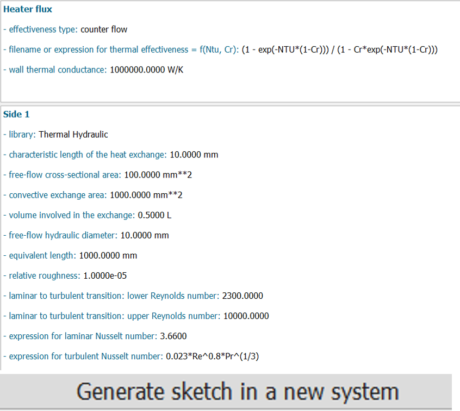 |
||||||||
| Heat exchange model calibration | One-click sketch generation | ||||||||
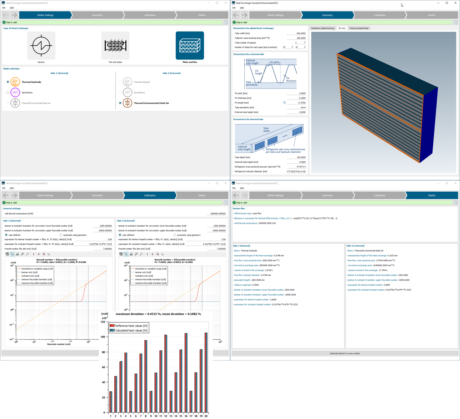
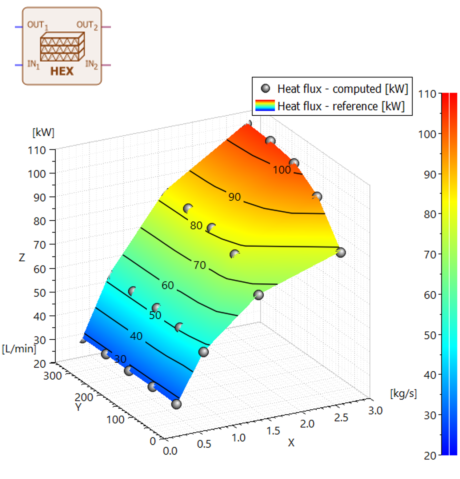
| * Application: Coolant radiator model from specifications | |||||||||
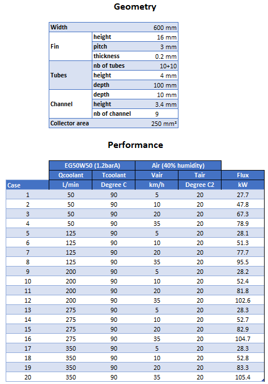 |
 |
 |
|||||||
| Starting from geometrical information and test data | Set up your heat exchanger in the HEX Assistant |
Generate and exploit | |||||||
| ◎ Compressor parameterization from specifications demo | |||||||||
| Two-Phase flow library | |||||||||
| - A new demonstrator with videos shows how to set up a compressor, from automatic data integration to automated parameterization validation through reference data Import | |||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Learn how to set up and validate a compressor model starting from a datasheet or test data | |||||||||
| ● Reproduce and customize the workflow thanks to videos showing all the steps | |||||||||
| ● Leverage all Simcenter Amesim features to save time and ultimately focus on the design activities | |||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| Available in Two-Phase flow library demos | Workflow-based demos with videos at each step | ||||||||
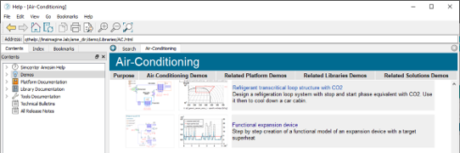
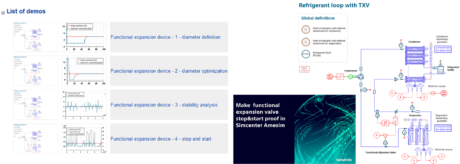
| ◎ Functional expansion device demo | |||||||||
| Air-Conditioning library | |||||||||
| - A new demonstrator with videos shows how to set up an expansion device with little or no data, including a dedicated yet simple control strategy for Stop and Start | |||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Learn how to set up and validate an HVAC loop expansion device controlling the superheat | |||||||||
| ● Reproduce and customize the workflow thanks to videos showing all the steps | |||||||||
| ● Leverage all Simcenter Amesim features to save time and ultimately focus on the design activities | |||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| Available in Two-Phase flow library demos | Workflow-based demos with videos at each step | ||||||||
| 2. Internal combustion engine and vehicle systems | |||||||||
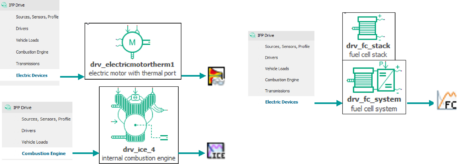
| ◎ IFP-Drive pre/post-processing improvements | |||||||||
| IFP-Drive |
|||||||||
| A. User can easily visualize electric machine tables | |||||||||
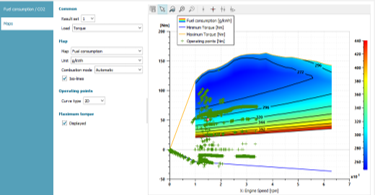
| B. User can analyze engine operating points over fuel consumption and pollutant maps | |||||||||
| C. User gets access to range estimation for fuel cell, hybrid and conventional vehicles | |||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| IFP-Drive library Apps | Brake-Specific Fuel Consumption analysis over WLTC | ||||||||
| Features | |||||||||
| ● Engine operating points can be plotted on top of fuel consumption or pollutant maps | |||||||||
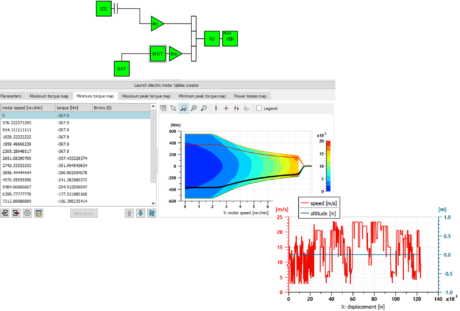
| ● Electric machine torque and efficiency tables can be visualized together | |||||||||
| ● Range is estimated for fuel cell, hybrid and conventional vehicles | |||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Facilitate analysis of engine efficiency over different gearboxes, control strategies, powertrain architectures, … | |||||||||
| ● Simplify understanding of how the electric machine model is parameterized | |||||||||
| ● Allow pre-sizing of hydrogen tank | |||||||||
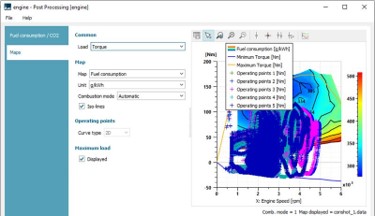 |
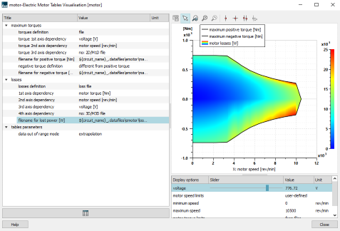 |
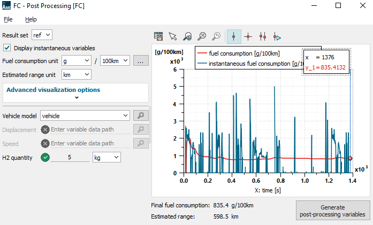 |
|||||||
| Engine operating points | Electric machine table visualization | Range estimation | |||||||
| PHEV powered with a Euro-6d-temp-compliant GDI engine | |||||||||
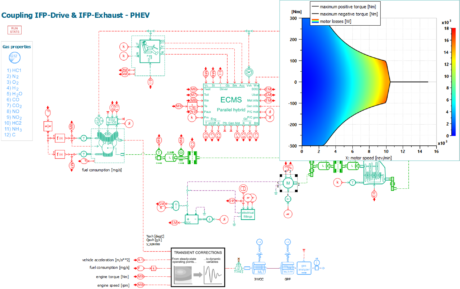 |
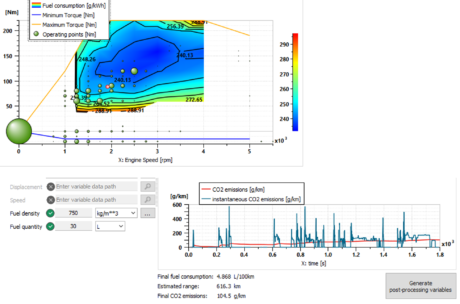 |
||||||||
| Setting up the model | Visualizing important design metrics on a WLTC driving cycle |
||||||||
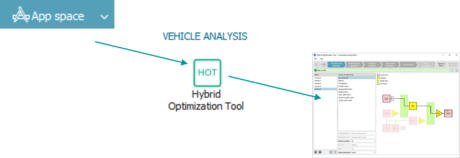
| ◎ Hybrid Optimization Tool updates | |||||||||
| IFP-Drive | |||||||||
| A. Parameterization is easier thanks to stacked tables and conditional parameters | |||||||||
| B. “Maximum velocity as a function of displacement” driving cycles can be simulated | |||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| App space > Vehicle analysis > Hybrid Optimization Tool | Stacked tables visualization | ||||||||
| Features | |||||||||
| ● Battery voltage limits are automatically computed | |||||||||
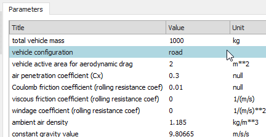
| ● Vehicle can be defined directly using S and Cx parameters | |||||||||
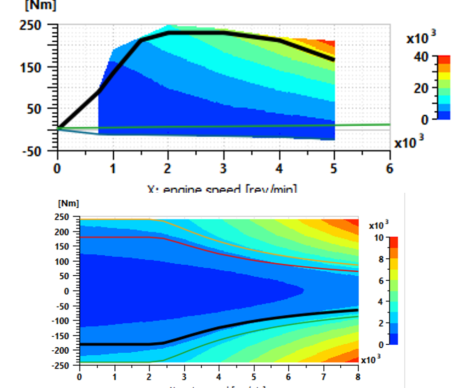
| ● Electric motor and engine tables are stacked | |||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Parameterizing is easier thanks to conditional parameters | |||||||||
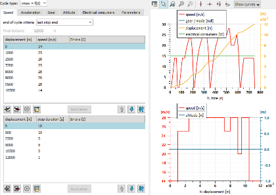
| ● Enabling truck and bus simulations with typical driving cycles | |||||||||
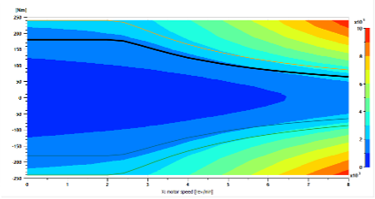
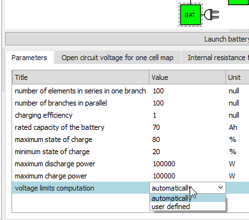 |
 |
||||||||
| Battery voltage limits | Vehicle aerodynamic coefs. | ||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| Stacked tables | Vmax driving cycles | ||||||||
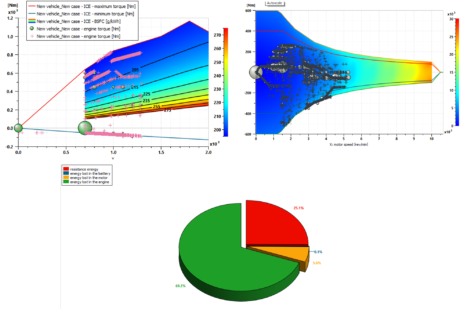
| Truck study in HOT | |||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| Parallel hybrid truck parameterization | Results analysis for an inter-urban delivery truck | ||||||||
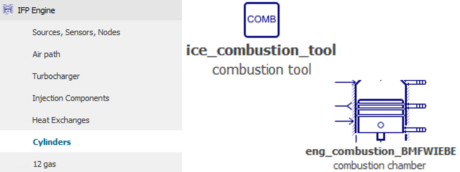
| ◎ High-frequency engine model update | |||||||||
| IFP-Engine | |||||||||
| A. Users rely on a single combustion chamber submodel for all empirical engine models | |||||||||
| B. Users can realistically account for dilution effects | |||||||||
| C. Users can use reduced-order models to characterize combustion behavior | |||||||||
 |
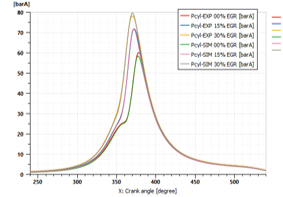 |
Variation of EGR rate at constant engine load and speed (10bar@2000rpm) | |||||||
| IFP-Engine > Cylinders | Typical cylinder pressure curve for diluted combustion | ||||||||
| Features | |||||||||
| ● Combination of BMF, heat release and Wiebe into a single submodel | |||||||||
| ● Compatibility with diluted combustion | |||||||||
| ● Combustion parameters can be defined through a reduced-order model (Neural network, RSM, polynomial, …) | |||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Simplify the combustion chamber submodel offer | |||||||||
| ● Align model capabilities with current technology trends | |||||||||
| ● Make it possible to model any type of combustion with a data-based approach | |||||||||
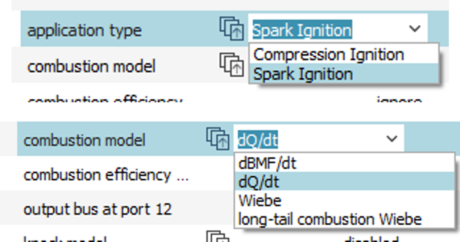 |
 |
 |
|||||||
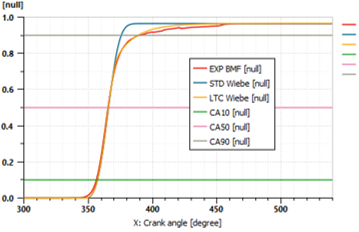
| Merge of empirical engine models | Wiebe law for diluted combustion | Combustion calibrated by a neural network |
|||||||
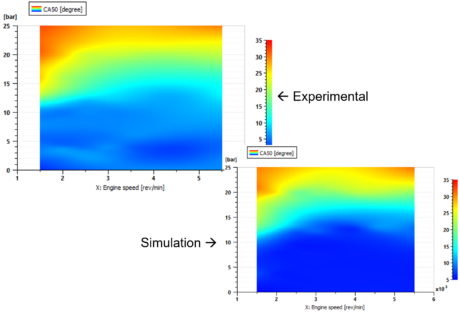
| Calibration of a Gasoline Direct Injection engine model with Exhaust Gas Recirculation | |||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
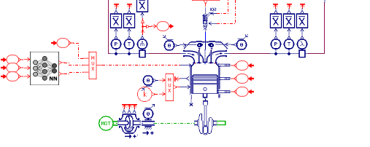
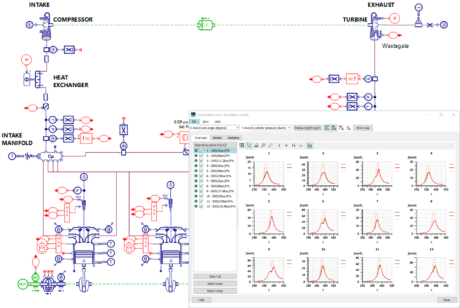
| Automatically calibrate the Wiebe model using the “Combustion tool” |
Use the combustion model to adjust the engine settings for injection, spark advance, EGR valve and turbocharger | ||||||||
| 3. Fluids | |||||||||
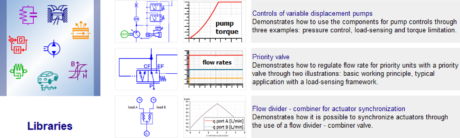
| ◎ New functional components demosFor Hydraulic library | |||||||||
| New functional components demos | |||||||||
| ● Basic systems to explore the behaviour of functional components | |||||||||
| ● Typical characteristic curves allowing a proper understanding of the main parameters | |||||||||
| ● Applicative examples showing the interest of the component in a typical usecase scenario | |||||||||
 |
 |
 |
|||||||
| Access | Basic systems and characteristic curves | Applicative examples | |||||||
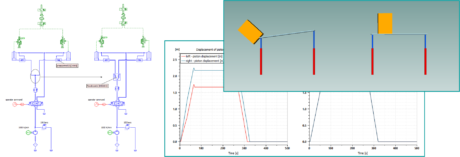
| Applicative examples | |||||||||
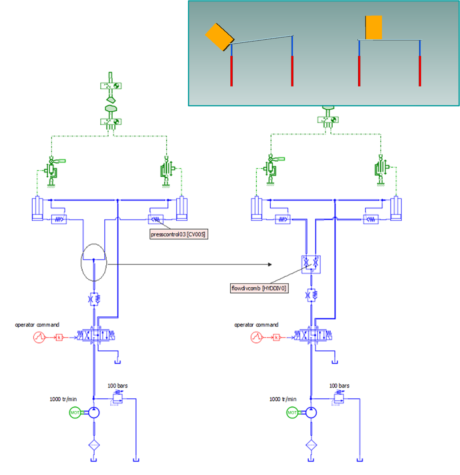 |
 |
 |
|||||||
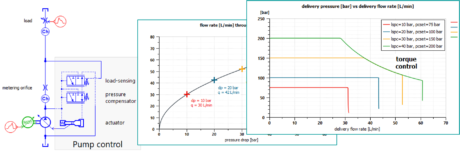
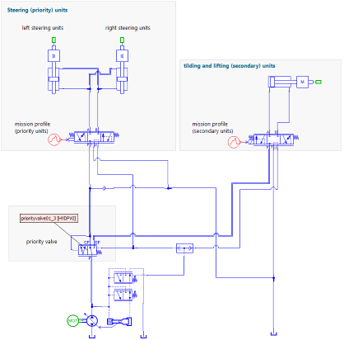
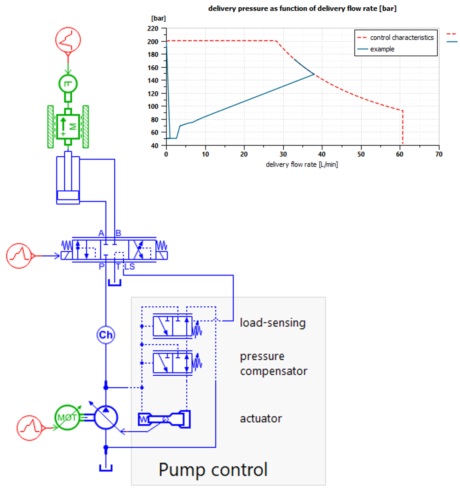
| Use of a Flow divider to insure the proper behaviour of a lifting system | Impact of a Priority valve on the behavior of a steering and lifting system. | Typical Pressure compensator and load sensing pump control | |||||||
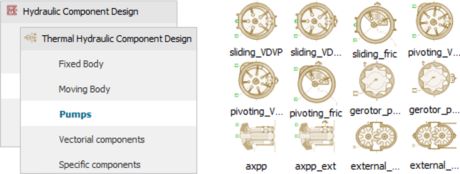
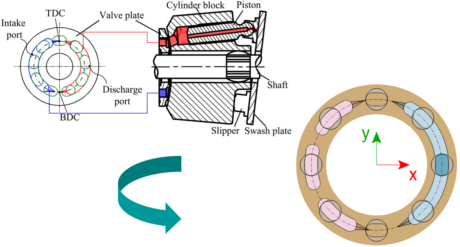
| ◎ Enhancement forPositive Displacement Pumps | |||||||||
| Positive displacement pump enhancement | |||||||||
| - Hydraulic Component Design &Thermal-hydraulic Component Design | |||||||||
| - Additional capabilities for volumetric pump integrated submodels (axial piston pump, external gear pump and vane pumps) | |||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
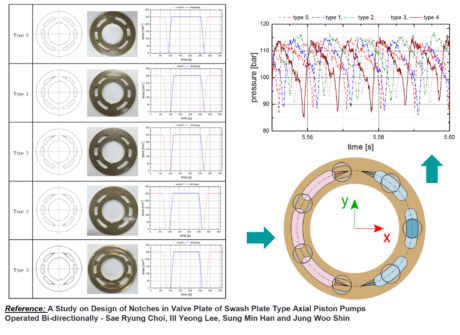
| Pumps folders in HCD and THCD libraries | Notches for Axial Piston Pump | ||||||||
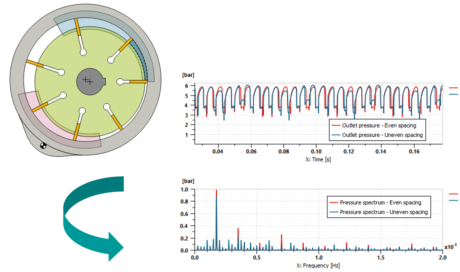 |
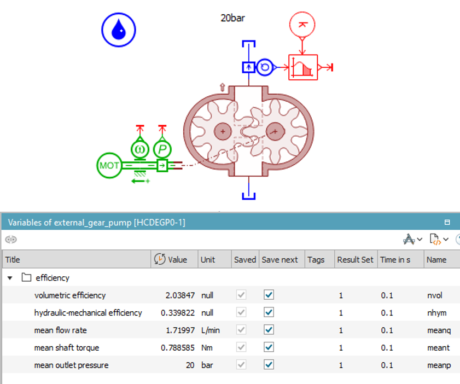 |
||||||||
| Vane pump - uneven spacing (CAD Import) | External Gear Pump Improvements | ||||||||
| Features | Design optimization for External Gear pump | ||||||||
| ● CAD import for vane pump with uneven vane spacing | 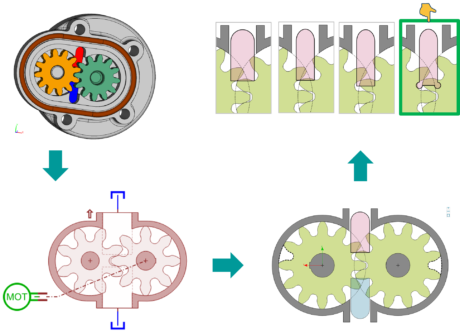 |
||||||||
| ● External gear pump with additional capabilities such efficiency and mechanical forces calculations | |||||||||
| ● Possibility to add notches on both sides of the inlet and outlet ports (even with multiple outlets) | |||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Allow to assess the impact of the vane spacing on the pump NVH performances using the CAD Import | |||||||||
| ● Provide multiple pump performances indicators | |||||||||
| ● Improve the axial piston pump model accuracy and behavior | |||||||||
| ● Enhance the pumps design representation | |||||||||
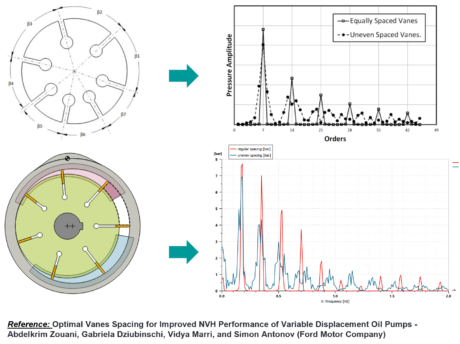 |
 |
||||||||
| NVH analysis for Variable displacement Vane pumps | Pressure analysis through AXPP port plate shape improvement | ||||||||
| 4. Electrical | |||||||||
| ◎ Electrical Basics usability improvements | |||||||||
| Electrical Basics |
|||||||||
| New electric basics components to simplify electric circuit creation : | |||||||||
| ● Dynamic voltage divider submodel |
|||||||||
| ● Imposing current preservation submodel |
|||||||||
| ● Variable load submodels: |
|||||||||
| - resistive |
|||||||||
| - inductive |
|||||||||
| - capacitive | |||||||||
| Electrical Basics library | |||||||||
| Single phase | |||||||||
| EBVDN01 voltage divider | 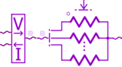 |
||||||||
| EBD2N01 double electric junction 2 ports | |
||||||||
| Three-phase |
|||||||||
| EB3SRV01 3 phase star variable R load without neutral connection | 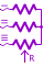 |
||||||||
| EB3SRLV01 3 phase star variable RL load without neutral connection | 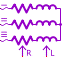 |
||||||||
| EB3SRLNV01 3-phase variation RL load with N node |  |
||||||||
| EB3DRCV01 3 phase delta variable RC load |  |
||||||||
| Features | |||||||||
| ● Imposed current conservation in circuits |
|||||||||
| ● Dynamic voltage divider with integrated node |
|||||||||
| ● Variable 3 phase with R, RL and RC loads |
|||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Reduce CPU time with fewer state variables |
|||||||||
| ● Reduce causality issue for faster and easier circuit creation |
|||||||||
| ● Simulate your load profile easily from measurements or 3rd party sources |
|||||||||
 |
 |
 |
|||||||
| Impose current preservation | Dynamic voltage divider | Variable load profile set-up | |||||||
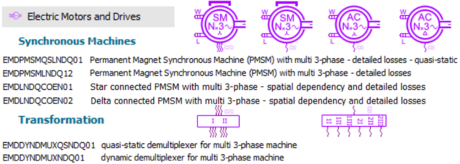
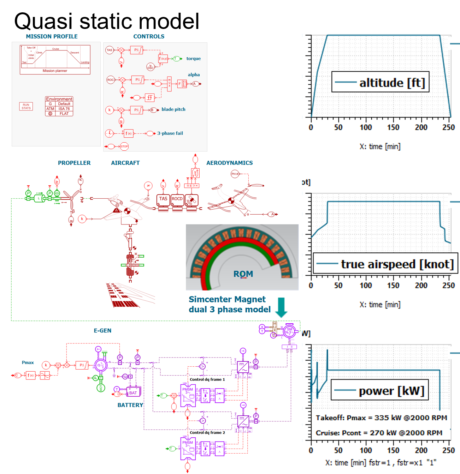
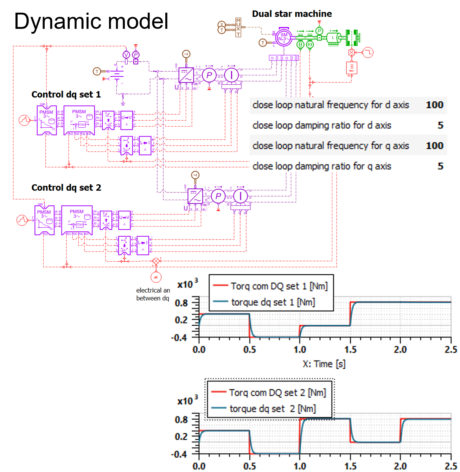
| ◎ Multi 3-phase PMSM major update | |||||||||
| Electric Motors and Drives | |||||||||
| Multi 3-phase PMSM with : |
|||||||||
| ● Quasi-static and detailed losses |
|||||||||
| ● dynamic and detailed losses |
|||||||||
| ● spatial harmonic and detailed losses |
|||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| Electric Motors and Drives library |
Dynamic block for 3-phase set and thermal | ||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
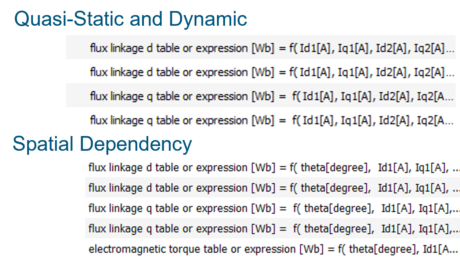
| Table or formula characteristic |
Advanced definition of losses | ||||||||
| Features | |||||||||
| ● Quasi-Static model |
|||||||||
| ● Spatial dependency model |
|||||||||
| ● Linear or non-linear magnetic characteristics |
|||||||||
| ● Detailed definition of losses for iron losses, winding resistances |
|||||||||
| ● Star / delta winding connection enumeration |
|||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Get fast evaluation of e-drive range on complex running cycle |
|||||||||
| ● Assess the machine thermal integration |
|||||||||
| ● Evaluate the Torsional Vibration Analysis of the e-drive |
|||||||||
| ● Use an accurate plant model for control development and validation |
|||||||||
 |
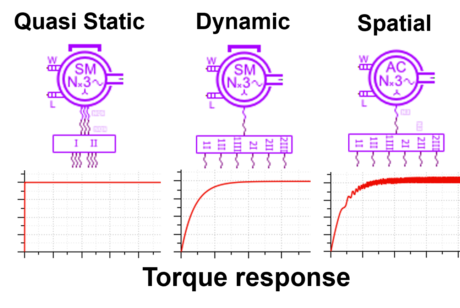 |
 |
|||||||
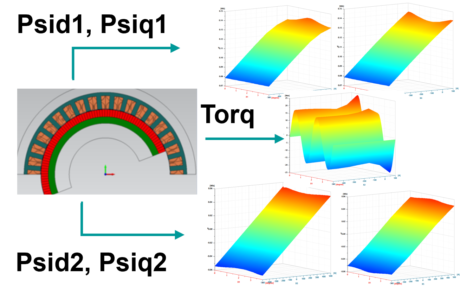
| Equivalent circuit model with FEM results |
Model scalability | Spatial dependency | |||||||
| Applicative examples |
|||||||||
| - Hybrid propulsion of dual star E-drive. Performance, range evaluation | |||||||||
| - E-drive control development and calibration | |||||||||
| - TVA analysis of a double star electric drive | |||||||||
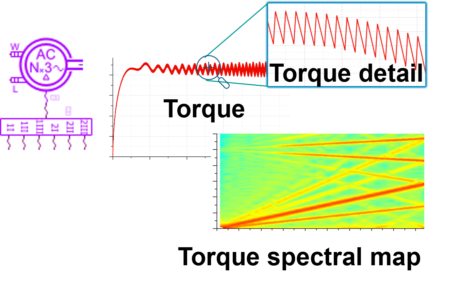
 |
 |
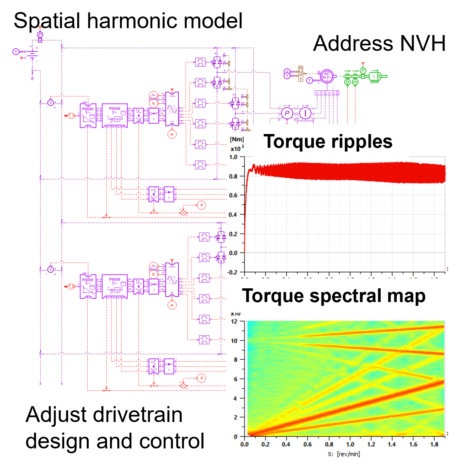 |
|||||||
| Validate a dual 3-phase machine performance in a serial hybrid aircraft propulsion |
E-drive control development and calibration Connect the plant model with 3rd party tools |
TVA analysis of a double star electric drive |
|||||||
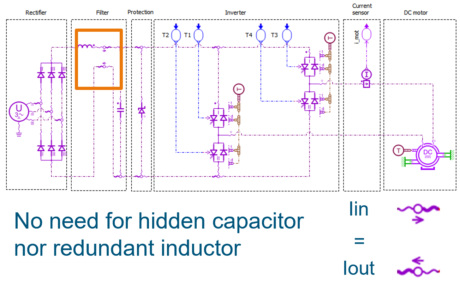
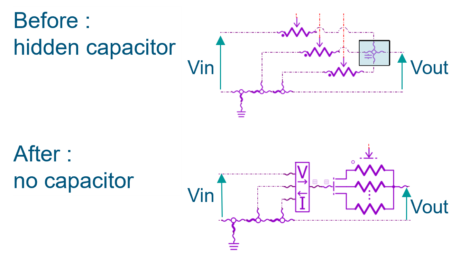
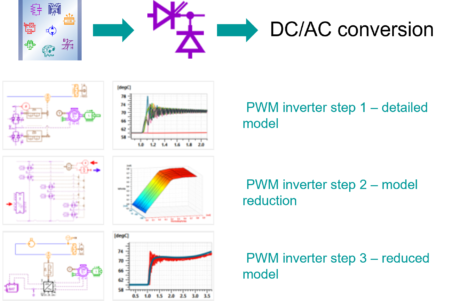
| ◎ Inverter reduction model with DOE demo set | |||||||||
| Electrical Static Conversion |
|||||||||
| ● Inverter reduction demo set using DOE |
|||||||||
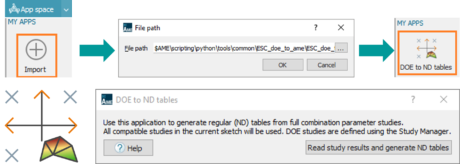
| ● DOE to ND tables app |
|||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| App space import > Data generation for system modeling | Demos > Library > ESC | ||||||||
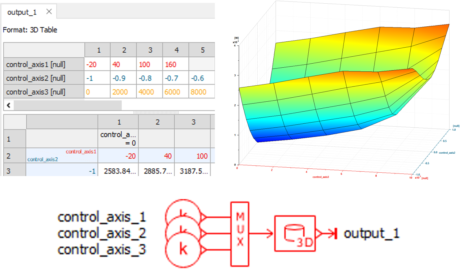
| Inverter reduction model with DOE – DOE to N-Dimension tables | |||||||||
| Features | |||||||||
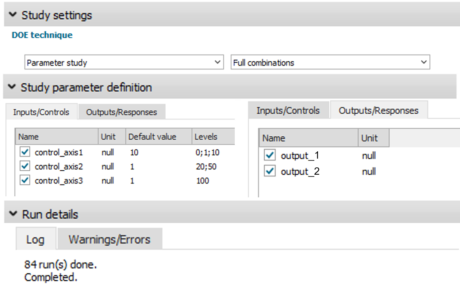
| ● DOE parameter study using full combination |
|||||||||
| ● App for automatic generation of Simcenter Amesim standard ND tables from DOE results |
|||||||||
| ● Demo set to illustrate the process with inverter model reduction |
|||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Generate reduced models rapidly using the DOE’s parallel processing capabilities |
|||||||||
| ● Generate tables easily for model reduction |
|||||||||
| ● Get a Real Time compliant reduced models from detailed models |
|||||||||
 |
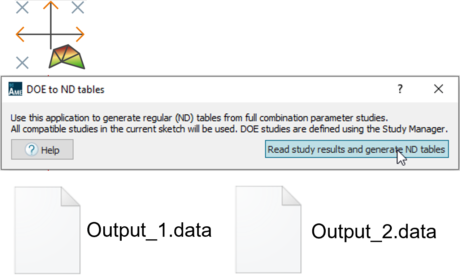 |
 |
|||||||
| DOE parameter study with full combination |
App for automatic ND table creation | Reuse easily ND tables for your simulation | |||||||
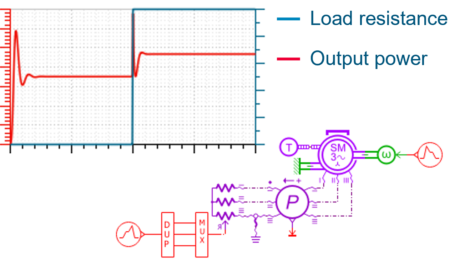
| Inverter reduction model with DOE – demo set | |||||||||
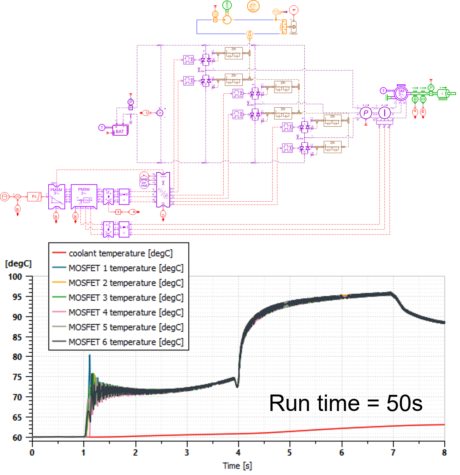 |
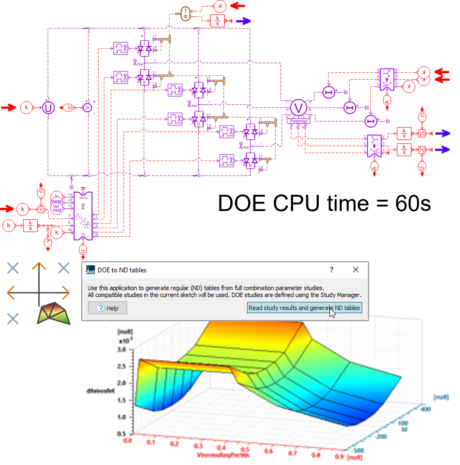 |
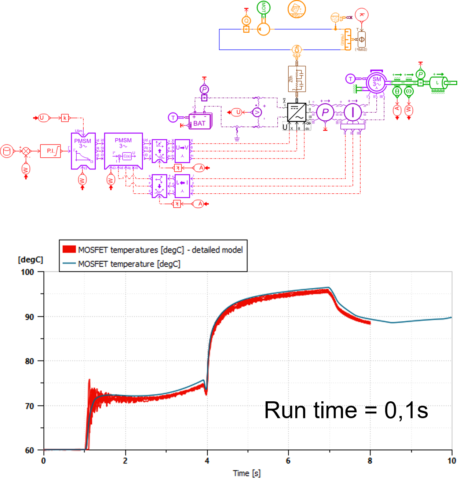 |
|||||||
| Step1 - Detailed inverter model with liquid cooling system | Step 2 - Model reduction using DOE and «DOE to ND tables» app | Step 3 - Fast simulation model | |||||||
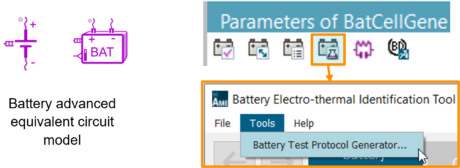
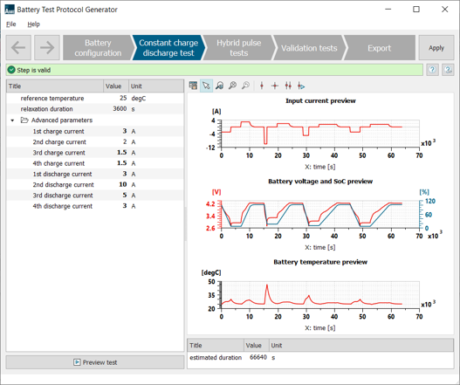
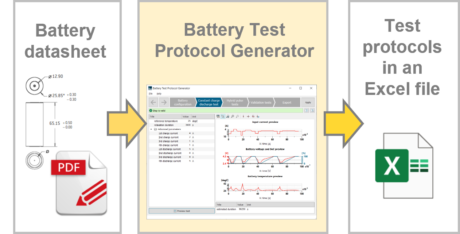
| ◎ Battery Test Protocol Generator | |||||||||
| Create test protocols to characterize the electrical and thermal behaviors of a battery | |||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| Tool accessible within the Battery Electro-thermal Identification Tool |
Tool interface | ||||||||
| Features | |||||||||
| ● Generation of test protocols from battery datasheet information |
|||||||||
| ● Simulation of all the tests with a pre-calibrated battery model |
|||||||||
| ● Test protocols exported into an Excel spreadsheet ready to be used by a test technician |
|||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Customize test protocols for your battery characterization |
|||||||||
| ● Preview the tests to avoid unexpected error before experiment |
|||||||||
| ● Get suitable test data for the Battery Electro-thermal Identification Tool to identify the electrical and thermal models |
|||||||||
 |
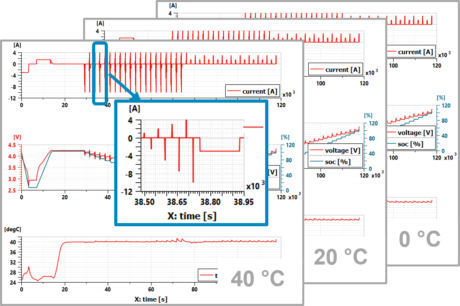 |
 |
|||||||
| Test protocols from battery datasheet | Simulation of all tests before experiment | Test data for model identification | |||||||
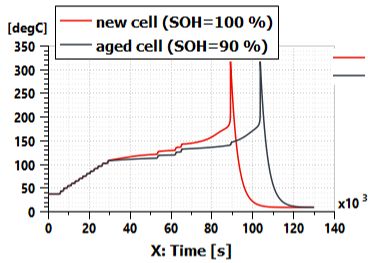
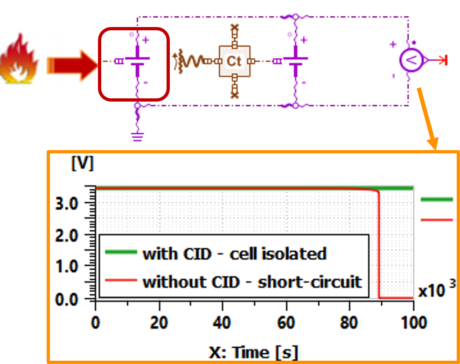
| ◎ Battery thermal runaway modeling enhancement | |||||||||
| Thermal runaway modeling considering : | |||||||||
| - initial state of charge (SOC) | |||||||||
| - state of health (SOH) | |||||||||
| - current interrupt device (CID) | |||||||||
 |
 |
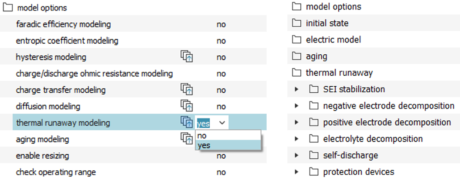
|
|||||||
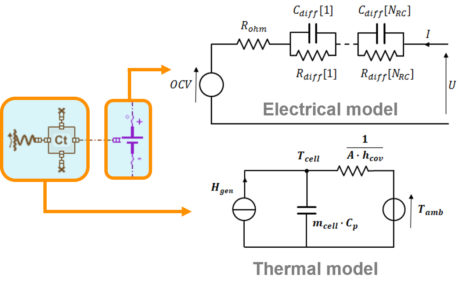
| Electric storage library |
In advanced equivalent circuit model of battery cell | Enable the thermal runaway modeling |
|||||||
| Features | |||||||||
| ● Consideration of the initial state of charge (SOC) |
|||||||||
| ● Consideration of the state of health (SOH) |
|||||||||
| ● Current interrupt device (CID) |
|||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Evaluate battery thermal runaway at different states of charge and different states of health |
|||||||||
| ● Simulate the electrical isolation of the cell in thermal runaway from the rest of the system |
|||||||||
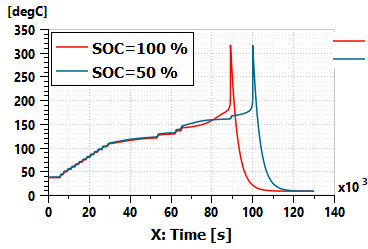 |
|
 |
|||||||
| Thermal runaway at different states of charge |
Thermal runaway at different states of health |
Thermal runaway with/without CID | |||||||
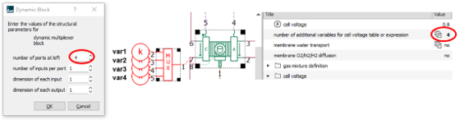
| ◎ Fuel Cell updates | |||||||||
| New multidimensional map-based Fuel Cell stackwith additional nonspecific input variables |
|||||||||
| - Map-based quasi-static voltage PEMFC stack | |||||||||
| - New multiplexed signal port allowing 10 additional non-specific table input variables |
|||||||||
 |

|
|
|||||||
| Fuel Cell Components library |
Voltage depends on up to 9 variables : 9 predefined / 10 non-specific |
Additional non-specific variables set up |
|||||||
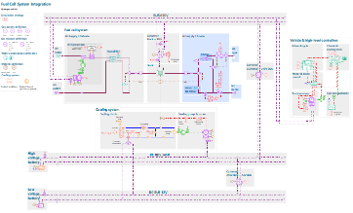
| Fuel cell system integration in a Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV) Updated Demo | |||||||||
| Features | |||||||||
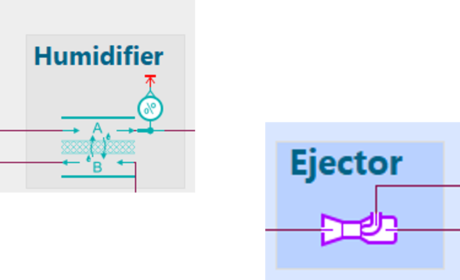
| ● Complete Balance of Plant (BoP): cooling loop, air and H2 supply loops with air compressor and ejector in the anode recirculation path |
|||||||||
| ● Detailed stack modeling including species transport across the membrane and diffusion across Gas Diffusion Layer (GDL) |
|||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Study cross-systems effects on vehicle range |
|||||||||
| ● Verify and optimize thermal management |
|||||||||
| ● Control the hydrogen purge on the anode side |
|||||||||
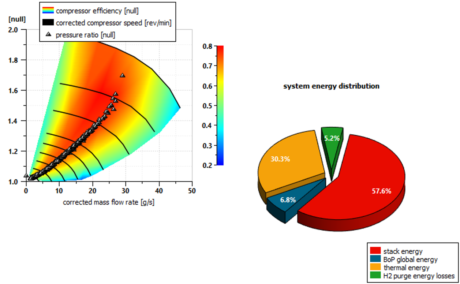
| ● Check the energy distribution in the system for different driving cycles |
|||||||||
 |
 |
 |
|||||||
| Integration of FC Stack + BoP with vehicle |
Membrane humidifier and ejector | Compressor efficiency and energy balance |
|||||||
| 5. Numerical and mechanics | |||||||||
| ◎ ROM Builder | |||||||||
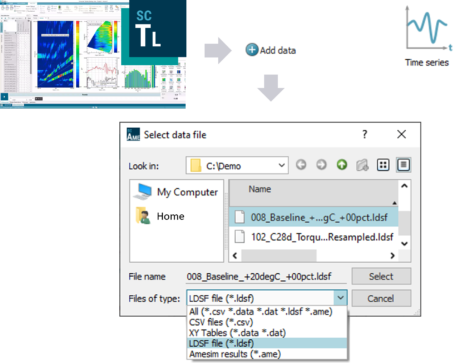
| Import time series from Simcenter Testlab | |||||||||
| Features | Import LDSF file in Time Series projects | ||||||||
| ● Import time series from Simcenter Testlab(.LDSF files) in Time series projects |
 |
||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Import native Simcenter Testlab data files |
|||||||||
| ● Sort variables automatically by sampling rate |
|||||||||
| ● Build static or dynamic Reduced Order Models (ROM) from measured data seamlessly |
|||||||||
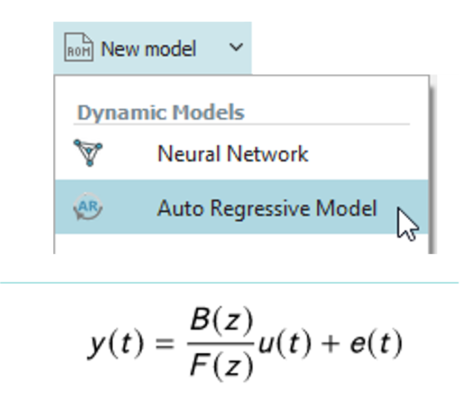
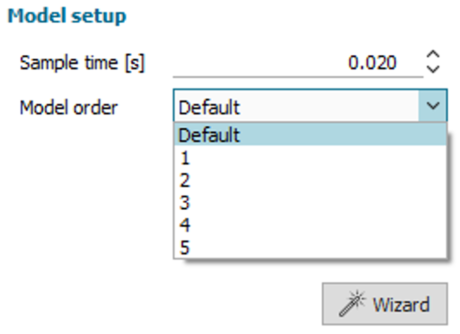
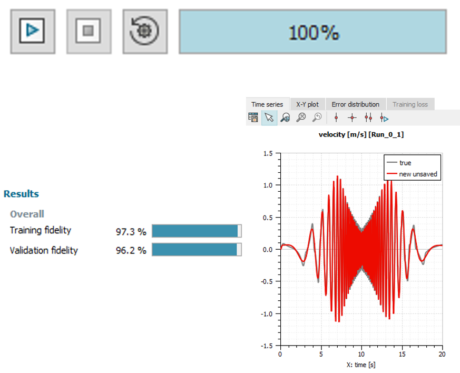
| Auto-regressive dynamic model | |||||||||
| Features | |||||||||
| ● New dynamic model type for linear, time invariant (LTI) behavior |
|||||||||
| ● Compatible with multiple inputs and outputs |
|||||||||
| ● Automatic order and sample time suggestion with the model wizard |
|||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Fit linear dynamics from time series easily, even with just a few training samples |
|||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| Select Auto-regressive model | Set up the model | ||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
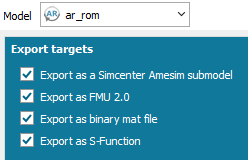
| Fit | Export | ||||||||
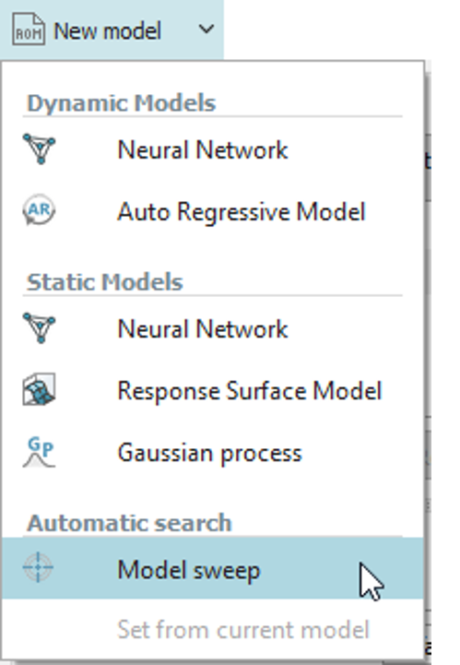
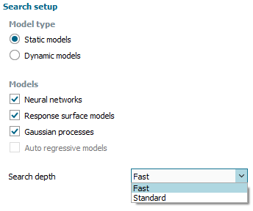
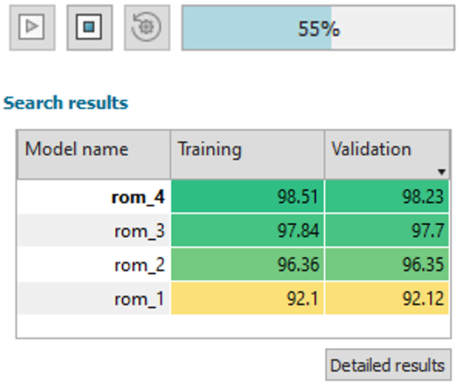
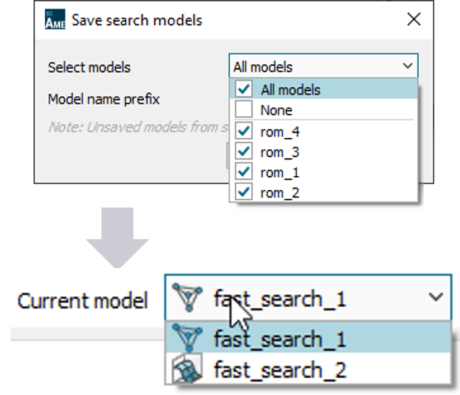
| Automated model search for static samples and time series | |||||||||
| Features | |||||||||
| ● Automatic exploration of models and hyperparameters |
|||||||||
| ● Available in Static samples and Time series projects |
|||||||||
| ● Search for filters to restrict or extend the model sweep |
|||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Find out the best type of reduced order model automatically |
|||||||||
| ● Obtain an accurate fit without manual search | |||||||||
| ● Benchmark performances of various ROM types |
|||||||||
| ● Reuse trained models for further analysis and training |
|||||||||
 |
|
||||||||
| Select Model sweep |
Filter search |
||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Search and track progress |
Save results |
||||||||
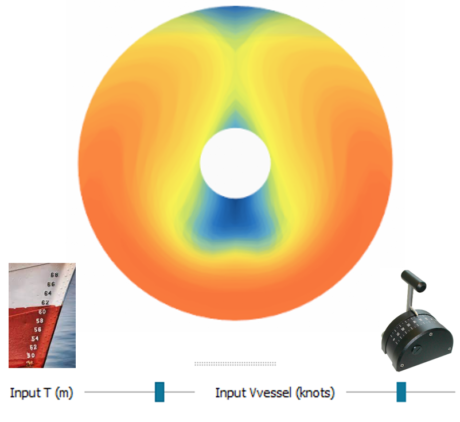
| ROM for 2D static fields | |||||||||
| Features | |||||||||
| ● Import static 2D fields from Simcenter STAR-CCM+ or another 3D or CFD tool |
|||||||||
| ● Fit a 2D ROM using Proper Orthogonal Decomposition and interpolation with Gaussian Processes |
|||||||||
| ● Easily check accuracy with metrics and plots |
|||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Predict 2D field for any combination of inputs within parameter range |
|||||||||
| ● Process 2D fields from Simcenter STAR-CCM+ seamlessly thanks to dedicated file exchange |
|||||||||
| ● Save predicted fields as images for further analysis |
|||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| Create a project | Import 2D snapshots | ||||||||
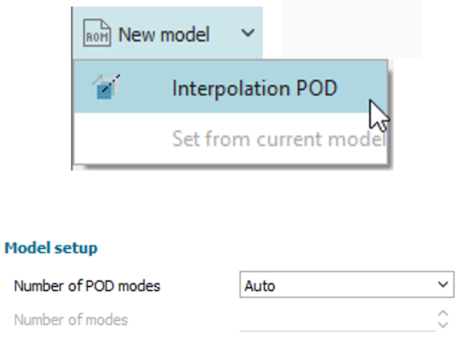 |
 |
||||||||
| Fit a 2D ROM | Predict field | ||||||||
| Visualize validation loss during training of neural networks | |||||||||
| Features | Validation loss can now be plotted during training | ||||||||
| ● Display of the validation loss in addition to the training loss during training of neural networks |
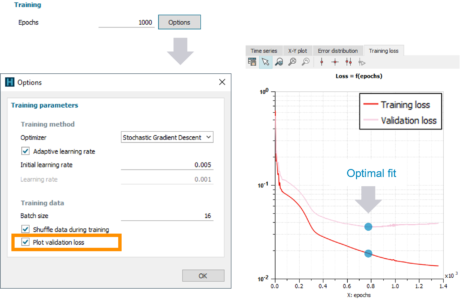 |
||||||||
| ● Available in Static samples and Time series projects |
|||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Enable detection of optimal fit and overfitting, that is to say when training loss continues to decrease while validation loss starts to increase | |||||||||
| Usability enhancements | |||||||||
| Features | |||||||||
| ● CSV import now handles files with text content or empty cells |
|||||||||
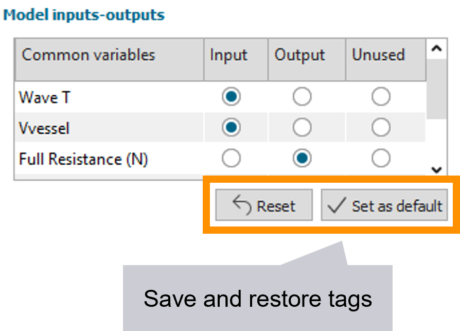
| ● Save and restore input and output tags in model setup |
|||||||||
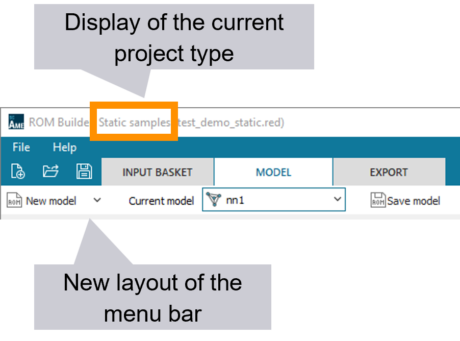
| ● Display current project type in the window title |
|||||||||
| ● New layout of the menu bar for easier navigation |
|||||||||
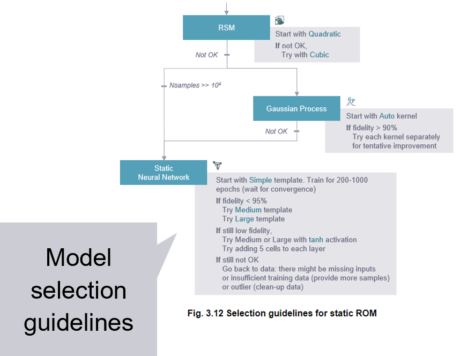
| ● Model selection charts in the documentation |
|||||||||
| Benefits | |||||||||
| ● Import most CSV files without re-formatting |
|||||||||
| ● Navigate intuitively in the ROM menus and actions |
|||||||||
| ● Learn how to select model types (alternative to using the automatic Model sweep) |
|||||||||
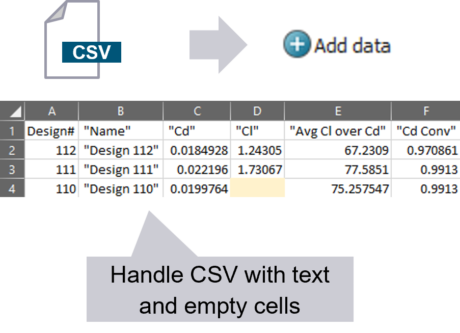 |
 |
||||||||
| CSV import improvements | Save input-output tagging | ||||||||
 |
 |
||||||||
| Easiest navigation | Documentation | ||||||||
| ◎ 2D Mechanical – converting new features | |||||||||
| ㅖ 72 | |||||||||
| ◎ Vehicle Dynamics standard maneuvers Manager and Analyzer | |||||||||
| ◎ Vehicle Loads Definition Tool | |||||||||
| ◎ 3D Mechanism On Chassis | |||||||||
| ◎ Electric Vehicle Torsional Vibration Analysis with detailed Electric Motor | |||||||||
| Electrical Basics |
|||||||||
| New electric basics components to simplify electric circuit creation : | |||||||||
| ● Dynamic voltage divider submodel |
|||||||||
| ● Imposing current preservation submodel |
|||||||||
| ● Variable load submodels: |
|||||||||
| - resistive |
|||||||||

